
Energy-efficient cooking appliances are transforming modern kitchens. Air fryers, such as the Cooking Air Electric Fryer, consume significantly less power than traditional deep fryers. They operate with wattages ranging from 1,400 to 1,700 watts, compared to the 2,500 watts of many ovens. This efficiency reduces electricity bills and environmental impact, especially with household visible air fryers that cook 20-30% faster. Additionally, models like the double heating element air fryer optimize heat distribution, further enhancing energy savings. Features like the LED digital control dual air fryer also provide precise cooking, minimizing energy waste.
How Each Appliance Works

Cooking Air Electric Fryer Basics
Air fryers, including models like the Cooking Air Electric Fryer, operate using high-speed air circulation technology. This mechanism distributes hot air evenly around the food, creating a crispy texture similar to traditional frying but with minimal oil. The core principle involves convective heat transfer, where hot air rapidly moves to cook food efficiently. This process removes moisture from the food’s surface, resulting in a golden-brown exterior.
Unlike deep fryers, air fryers require shorter preheating and cooking times, which contributes to their energy efficiency. For instance, they can reduce preheating times by up to 75% and cooking times by up to 50%. The Cooking Air Electric Fryer exemplifies this efficiency, consuming between 1.4 to 1.8 kWh per use, making it a cost-effective and eco-friendly choice for households.
Tip: Lightly coating food with oil before air frying enhances crispiness while maintaining a healthier cooking method compared to deep frying.
Deep Fryer Basics
Deep fryers rely on hot oil immersion to cook food. This method ensures even heat penetration, producing a consistent texture and flavor. The appliance uses precise temperature control to maintain optimal cooking conditions, which can lead to higher energy consumption. Larger models or those designed for high output often require more power to operate effectively.
Deep fryers typically consume between 1.0 to 3.0 kWh per use, depending on their size and features. Features like quick recovery times, where the fryer rapidly reheats oil after food is added, further contribute to energy usage. While these appliances excel in cooking large batches, their longer heat-up times and reliance on oil make them less energy-efficient compared to air fryers.
Note: Regular maintenance, such as cleaning oil filters and replacing old oil, can improve the efficiency and lifespan of deep fryers.
Energy Consumption Comparison

Wattage and Power Usage
The wattage of an appliance directly impacts its energy consumption. Deep fryers typically operate at 2,000 watts, making them one of the more energy-intensive kitchen appliances. In contrast, air fryers, such as the Cooking Air Electric Fryer, consume around 1,500 watts. This difference in power usage translates to significant energy savings over time.
Air fryers also benefit from their ability to maintain consistent heat levels without requiring additional energy to reheat oil, as deep fryers often do. This efficiency makes air fryers a more sustainable choice for households aiming to reduce electricity bills.
Cooking Times and Heat Retention
Cooking times and heat retention play a crucial role in energy efficiency. Air fryers excel in this area due to their rapid preheating and cooking capabilities. For example:
- Air fryers can reach 300°F in under 3 minutes, while a standard oven takes approximately 15 minutes to preheat.
- Cooking times vary depending on the food. Bacon takes 8-12 minutes, a whole chicken up to 65 minutes, and vegetables 5-15 minutes.
Air fryers retain most of their heat during cooking, minimizing energy loss to the surrounding environment. This feature allows them to cook food faster than traditional methods. By keeping heat inside, air fryers like the Cooking Air Electric Fryer ensure efficient energy use, making them a practical choice for energy-conscious consumers.
Real-World Examples of Energy Use
Real-world testing highlights the energy efficiency of air fryers compared to deep fryers. For instance:
- A Sayona Air Fryer uses 0.32 kWh for 32 minutes of cooking, costing approximately 6 Ksh.
- A pressure cooker, by comparison, consumes 0.42 kWh for 1 hour of cooking, costing about 10 Ksh.
The following table further illustrates the energy consumption differences:
| Cooking Method | Energy Consumption (Watts) | Energy Savings (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Deep Fryer | 2000 | N/A |
| Air Fryer (SAF-4567) | 1500 | 30-40% |
| Chicken Wings | N/A | 62% |
| French Fries | N/A | 45% |
| Fish Fillets | N/A | 50% |
These examples demonstrate that air fryers not only consume less energy but also deliver substantial savings, particularly for commonly cooked items like chicken wings and French fries.
Factors Influencing Energy Efficiency
Cooking Volume and Batch Size
The amount of food cooked at one time significantly impacts energy efficiency. Air fryers, such as the Cooking Air Electric Fryer, excel in small to medium batch sizes due to their rapid heating and cooking capabilities. They use hot air circulation to cook food evenly and quickly, reducing prep time and energy consumption.
Deep fryers, on the other hand, are better suited for high-volume cooking. Their ability to maintain consistent oil temperatures makes them ideal for busy kitchens or large gatherings. However, this advantage comes at the cost of higher energy usage, as deep fryers require more power to heat and sustain large quantities of oil.
- Key Points:
- Air fryers heat up faster, saving time and energy for smaller batches.
- Deep fryers are more efficient for cooking large quantities but consume more electricity overall.
- Air fryers typically operate between 1,200-1,800 watts, leading to lower electricity bills.
- Deep fryers require longer preheating and cooking times, increasing energy consumption.
Air fryers also reduce grocery costs by using minimal oil, making them a more economical choice for energy-conscious households.
Frequency of Use
The frequency of appliance use directly affects energy efficiency. For occasional use, air fryers prove to be more energy-efficient due to their shorter cooking times and lower power requirements. Frequent use of deep fryers, however, can lead to higher energy bills because of their prolonged preheating and cooking durations.
Households that cook smaller portions regularly benefit from air fryers. Their ability to cook quickly without compromising food quality makes them a practical choice for daily use. In contrast, deep fryers are better suited for commercial kitchens or homes that frequently prepare large meals.
Tip: For optimal energy savings, choose an appliance that aligns with your cooking habits and meal sizes.
Preheating Requirements
Preheating plays a crucial role in determining energy efficiency. Air fryers heat up rapidly, reaching cooking temperatures in just a few minutes. This quick preheating process minimizes energy waste and reduces overall cooking time.
Deep fryers, however, require more time to heat oil to the desired temperature. This extended preheating period increases energy consumption, especially when cooking multiple batches. The advanced technology in air fryers, such as the Cooking Air Electric Fryer, allows for faster cooking times, further enhancing energy savings.
- Comparison:
- Air fryers: Minimal preheating time, lower energy usage.
- Deep fryers: Longer preheating time, higher energy consumption.
By reducing preheating requirements, air fryers offer a more energy-efficient solution for modern kitchens.
Maintenance and Cleaning
Proper maintenance and cleaning significantly influence the energy efficiency of both appliances. Air fryers require minimal upkeep, as they use little to no oil. Regular cleaning of the basket and interior ensures optimal performance and prevents energy waste.
Deep fryers demand more extensive maintenance. Frequent oil changes and cleaning of filters are necessary to maintain efficiency. Neglecting these tasks can lead to increased energy consumption and reduced appliance lifespan.
Note: Keeping appliances clean not only improves energy efficiency but also enhances food quality and safety.
Air fryers, with their simpler maintenance requirements, provide a more convenient and energy-efficient option for households.
Additional Considerations
Cost of Operation
The cost of operating cooking appliances depends on their energy consumption and frequency of use. Air fryers, with wattages ranging from 1,400 to 1,800 watts, consume less electricity than deep fryers, which often require 2,000 watts or more. Over time, this difference leads to noticeable savings on electricity bills.
Cooking time also plays a role in operational costs. Air fryers cook food faster than ovens or deep fryers, reducing energy usage per session. However, for extended cooking durations, air fryers may consume more energy due to their continuous power requirement. Households that prioritize energy efficiency benefit from air fryers, especially for smaller meals or quick recipes.
Tip: To maximize savings, use appliances that align with your cooking habits and meal sizes.
Environmental Impact
Cooking methods impact air quality and emissions. Air fryers produce significantly fewer volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and particulate matter (PM) compared to deep frying. For example:
| Cooking Method | VOCs (ppb) | PM (µg/m³) |
|---|---|---|
| Pan Frying | 260 | 92.9 |
| Deep Frying | 230 | 7.7 |
| Air Frying | 20 | 0.6 |
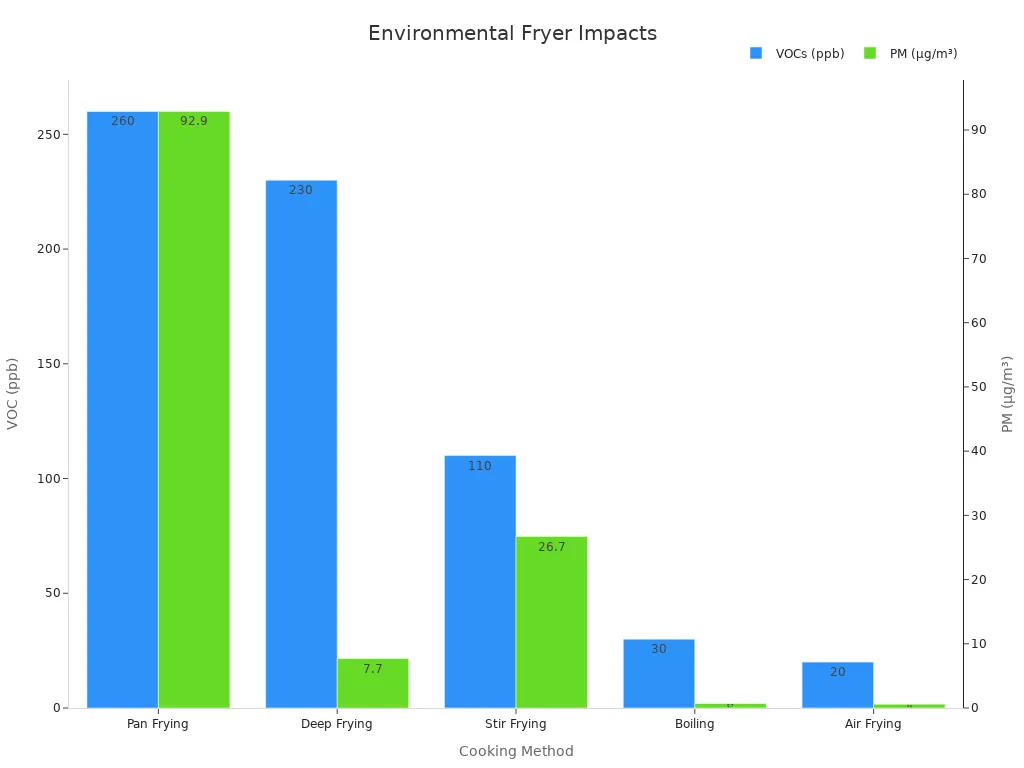
Air fryers emit only 20 ppb of VOCs, compared to 230 ppb from deep fryers. Their PM output is also minimal, at just 0.6 µg/m³. These figures highlight the environmental advantages of air fryers, making them a cleaner choice for eco-conscious households.
Versatility and Practicality
Modern cooking appliances offer diverse features to enhance versatility and efficiency. Air fryers excel in preparing a wide range of dishes, from crispy snacks to roasted vegetables, using minimal oil. Their compact design and rapid cooking capabilities make them practical for everyday use.
Other appliances, such as induction cooktops, showcase superior energy efficiency and safety. They boil water in just two minutes and include automatic shutoff features, eliminating open flames. Dual fuel ranges combine gas cooktops with electric ovens, ensuring precise temperature control and even heat distribution.
Note: Choosing versatile appliances like air fryers or induction cooktops ensures efficient cooking while reducing energy consumption.
Air fryers outperform deep fryers in energy efficiency due to their lower power consumption and quicker cooking times. They align with modern trends favoring healthier and more sustainable cooking methods. Innovations in air fryer technology, such as improved energy efficiency, will likely increase their popularity. Consumers should evaluate their cooking habits, meal sizes, and energy costs to choose the most suitable appliance.
FAQ
1. Which appliance is better for small households?
Air fryers suit small households due to their compact size, faster cooking times, and lower energy consumption. They efficiently handle small to medium batch sizes.
2. Do air fryers require special maintenance?
Air fryers need minimal maintenance. Regularly clean the basket and interior to ensure optimal performance. Avoid abrasive cleaners to maintain the non-stick coating.
3. Can deep fryers be energy-efficient for large gatherings?
Deep fryers perform well for large gatherings. Their ability to maintain consistent oil temperatures makes them efficient for cooking large quantities, despite higher energy usage.
Post time: Jun-04-2025

